Software and Code
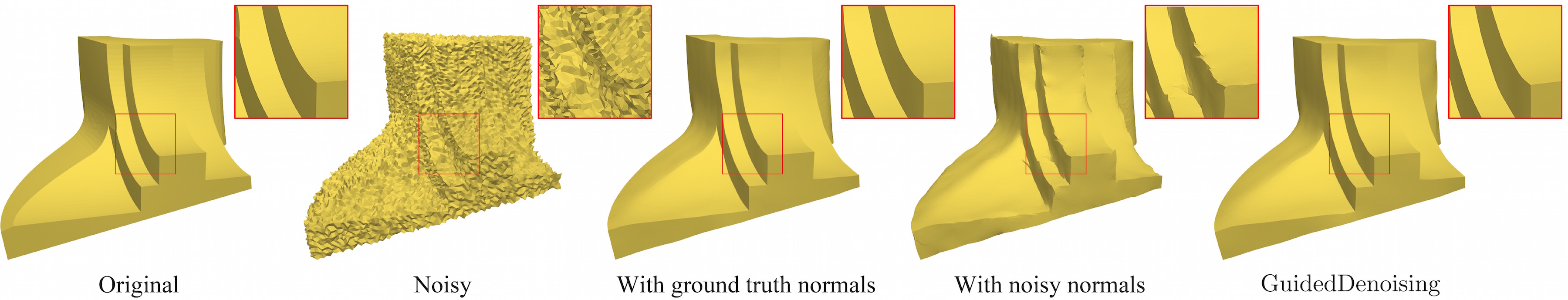
Guided Mesh Normal Filtering
GuidedDenoising is a C++ library for mesh denoising, where the noise type could be any types like gaussian noise and impulsive noise. This library also includes the implementations of some classical denoising algorithms include bilateral mesh denoising, Non-iterative, feature-preserving mesh smoothing, Fast and Effective Feature-Preserving Mesh Denoising, Bilateral Normal Filtering for Mesh Denoising, Mesh denoising via L0 minimization. GuidedDenoising is released under GNU LGPL V3 License.
Download: GuidedDenoising code
Local Barycentric Coordinates
LBC is a C++ library for computing local barycentric coordinates. LBC is released under GNU General Public License.
Download: LBC code
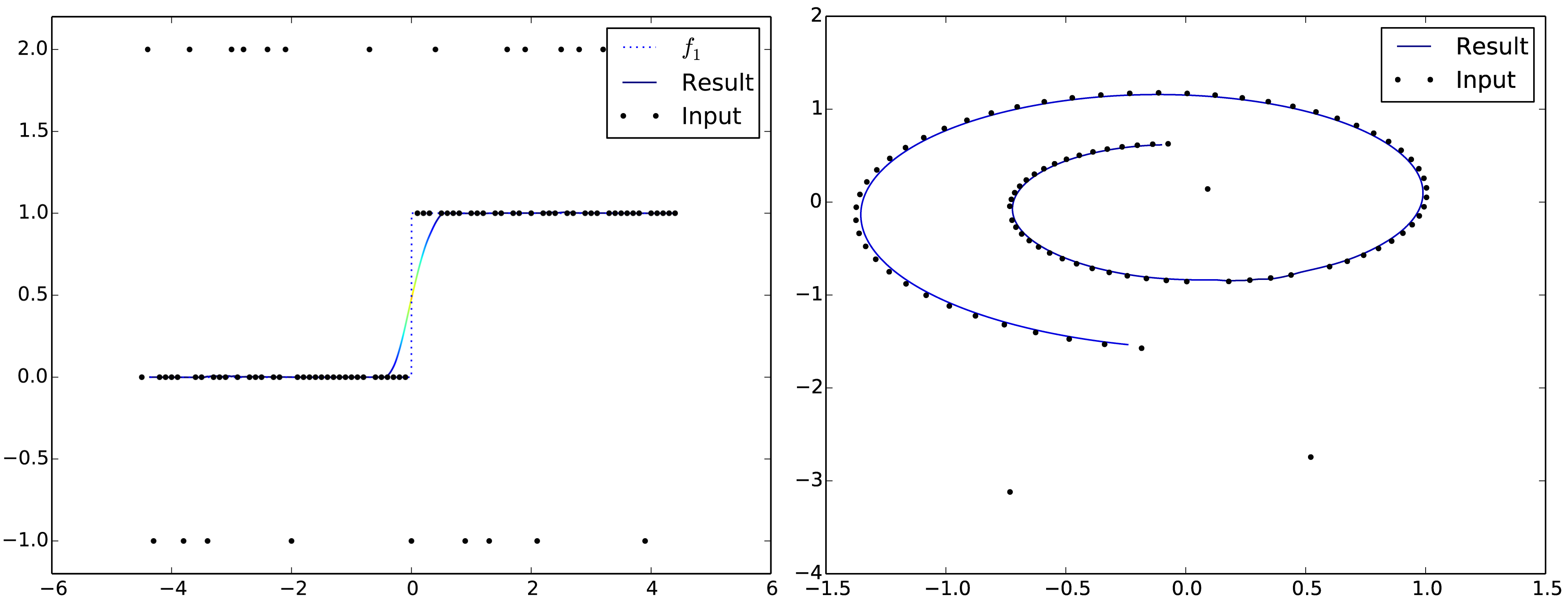
\(\ell_1\) Subdivision Scheme for noisy curve and surface datas
\(\ell_1\)-Subdivision is a Python library for curve and surface denoising.
Download: \(\ell_1\)-Subdivision code
Multichannel Total Variation Minimization
MTV—\(\ell_1\) Solver is matlab library for solving multichannel total variation based models, especially for image restoration.
Download: MTV—\(\ell_1\) Solver code
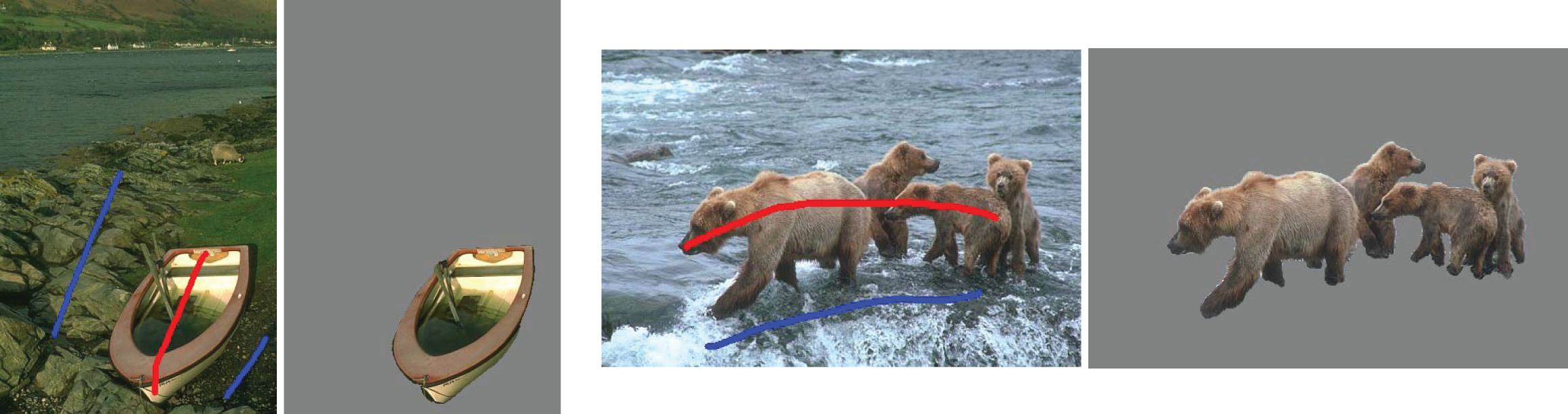
Convex Active Contour for Interactive Image Segmentation
CAC—Segmentation is a software for interactive image segmentation by inputing foreground and background seeds as shown in the above figures as red curve and blur curve.
Download: CAC—Segmentation code
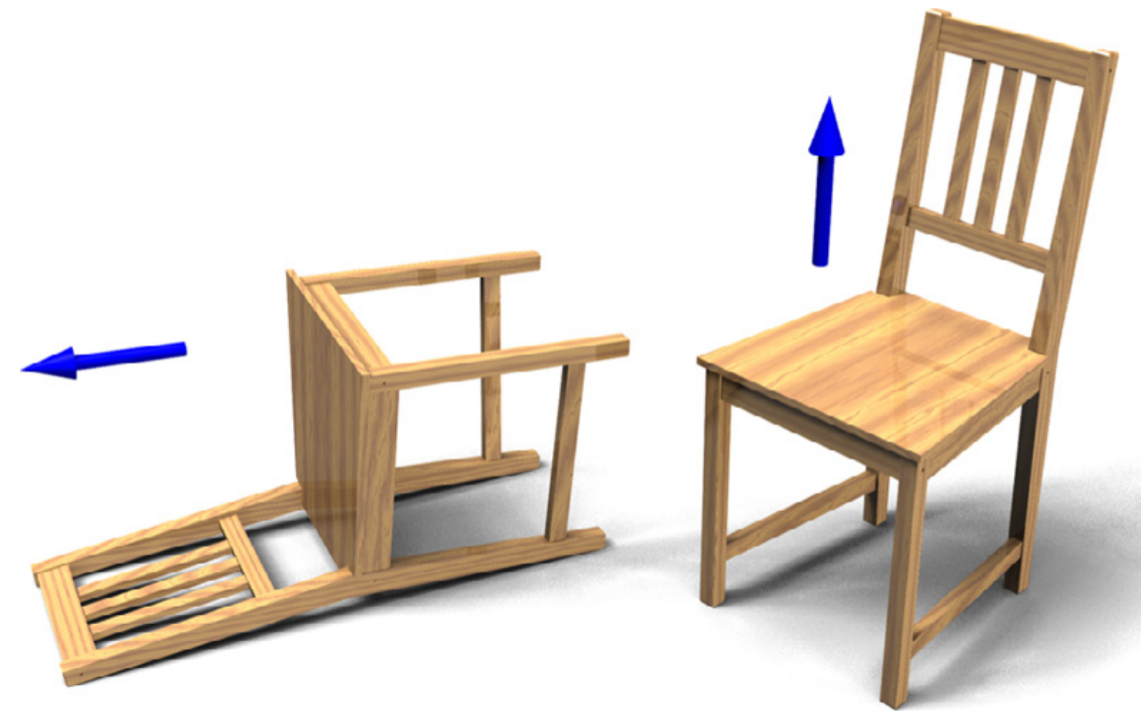
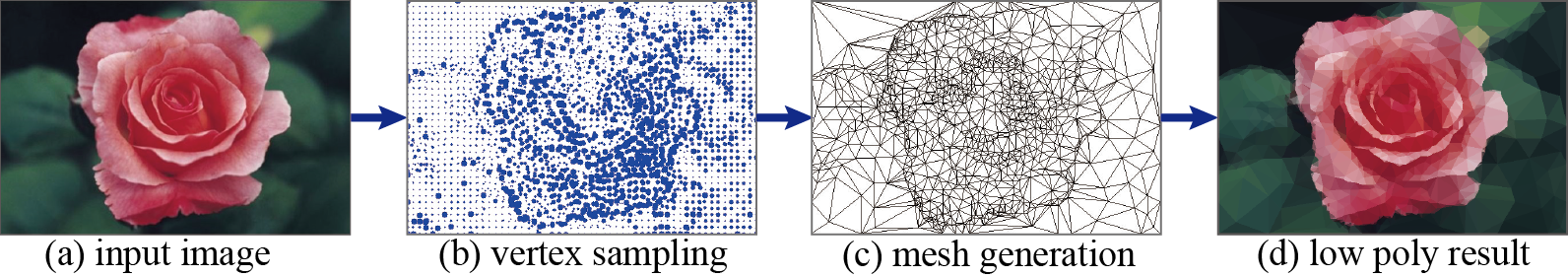
Low-poly illustration generation from images
Algorithm overview. Given an input image (a), we first sample pixels and rank them according to their importance of preserving the image structure (b). We can see that the points on the edges are much more important. Then a Delaunay triangulation is constructed from the first K points according to user's selection (c). Finally, we render the color of each triangle to generate a low-poly illustration with a artistic looking.
Download: Low-poly illustration from images code
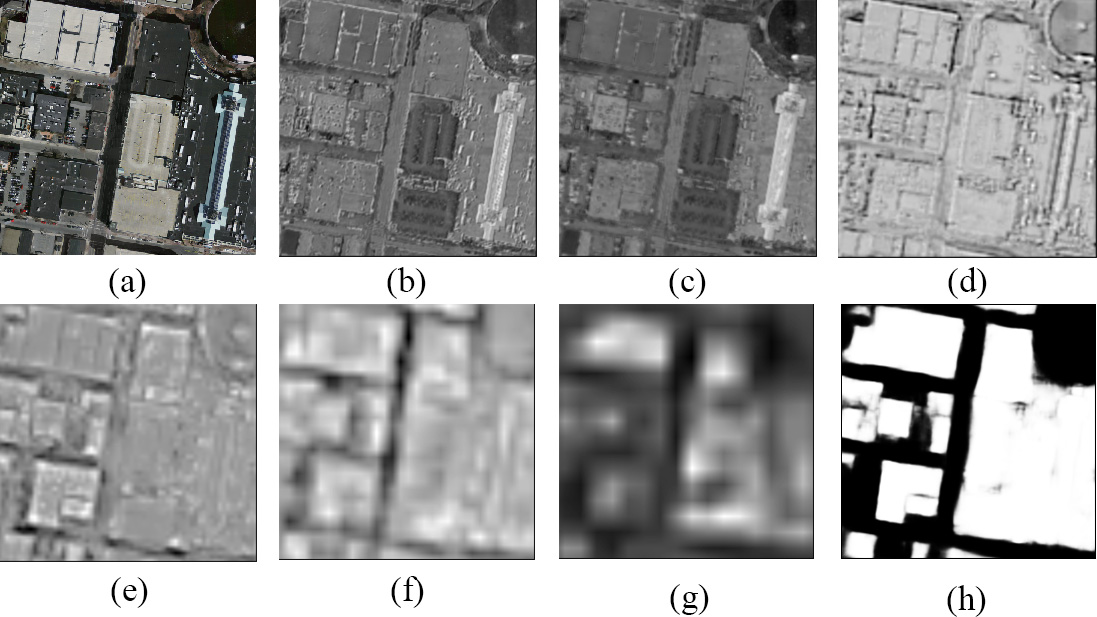
HF-FCN
(a) Input aerial image. (b - c) Feature maps generated from shallow layers with fine spatial resolution but low level semantic information. (d - e) The feature maps at middle layers correspond to certain intermediate-level features. (f - g) Deep layers generate coarse feature maps with high-level semantic information. (h) Integrating all these feature maps, we get predicted labelling map.
Download: HF-FCN code
Upright orientation estimation
Upright Orientation of 3D Shapes with Convolutional Networks.
Download: Upright orientation estimation with CNN code
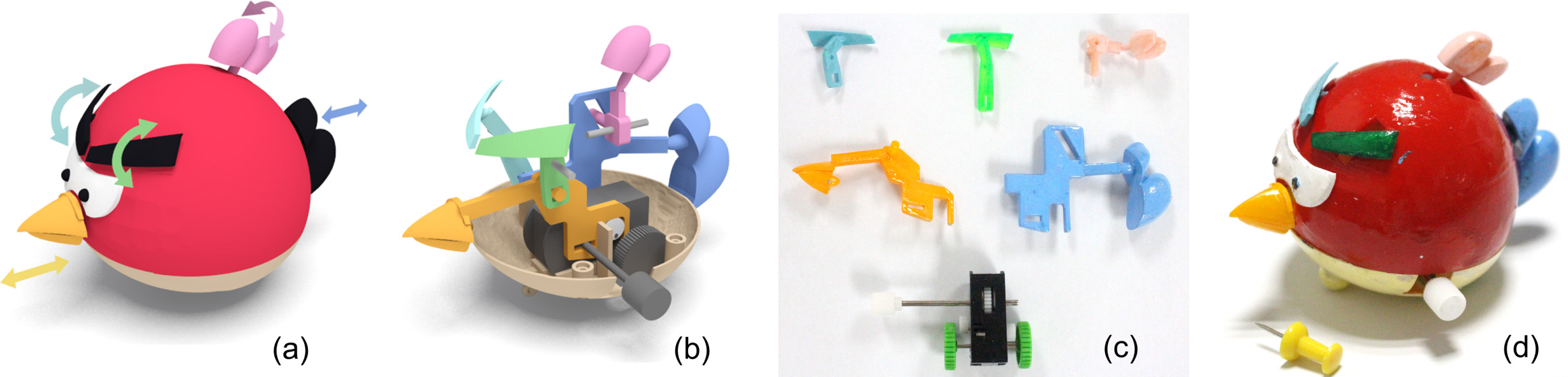
Computational design of wind-up toys
(a) Input model with user-provided parts geometry and motion; (b) wind-up mechanism constructed by our method; (c) 3D-printed parts (top two rows) and spring motor (bottom); and (d) assembled toy (9.2 x 6.7 x 6.4cm^3; and 16.1g shell + 7.9g motor + 7.3g mechanism).
Download: Computational design of wind-up toys code
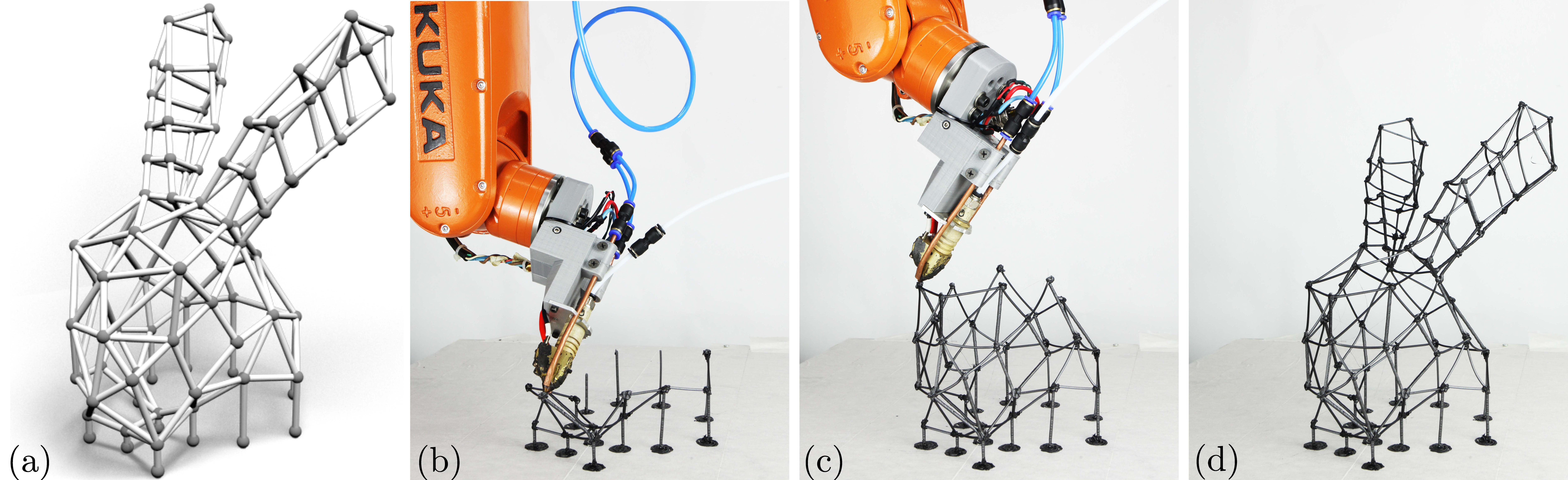
FrameFab: Robotic Fabrication of Frame Shapes
Given a frame shape (a), we propose an algorithm for generating a feasible fabrication sequence of struts which guarantees that the already-printed part is in a stable equilibrium state and that the extrusion head avoids collision with the printed part at all fabrication stages. This is verified by a built prototype robotic fabrication system consisting of a 6-axis KUKA robotic arm with a customized extrusion head: (b) and (c) are intermediate fabrication states and (d) is the final fabrication object for the given frame shape (a).
Download: FrameFab code
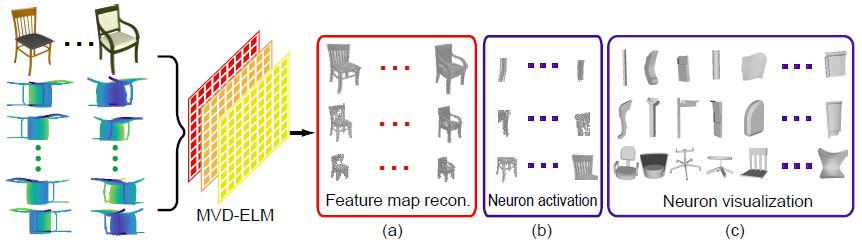
Projective Feature Learning for 3D Shapes with Multi-View Depth Images
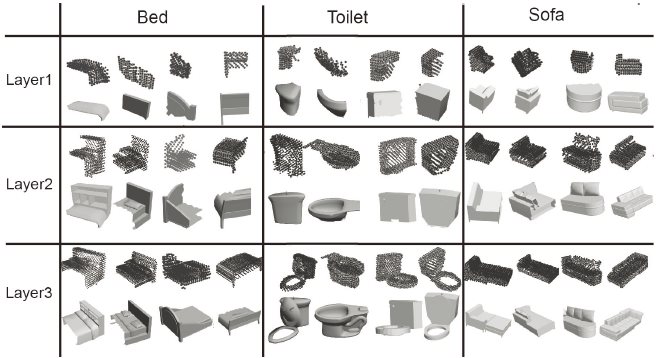
We propose an projective feature learning method, called MVD-ELM, for learning 3D shape features from multi-view depth images. (a) Our network ensures that the unprojection of the feature maps in each layer together form a reconstruction of the input 3D shapes. (b) Point clouds reconstructed from the maximally activated regions of feature maps (neurons). (c) Visualization of cropped shape parts according to the maximally activated neurons.
Download: MVD-ELM code
Garment Personalization via Identity Transfer
We present a method for transferring the identity of a given subject to a target image for try-on experience of clothes. The method involves cloning the user's identity into a catalogue of model images wearing the desired garments.
Download: Garment Personalization code
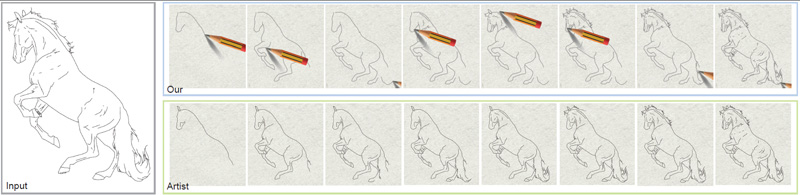
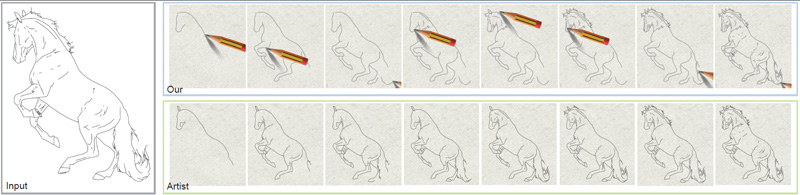
Animated Construction of Line Drawings
Guided by sketching principles, we derive a plausible stroke order of an input vectorized line drawing (left) to automatically animate the sketching (right top). A user study shows that the inferred order is comparable to the order used by an artist (right bottom).
Download: Animated construction of line drawings code
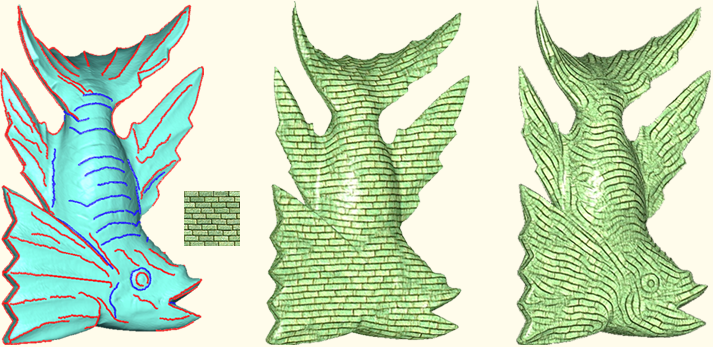
Feature-Aligned Shape Texturing
The essence of a 3D shape can often be well captured by its salient feature curves. In this paper, we explore the use of salient curvesin synthesizing intuitive, shape-revealing textures on surfaces. Our texture synthesis is guided by two principles: matching the direction of the texture patterns to those of the salient curves, and aligning the prominent feature lines in the texture to the salient curves exactly. We have observed that textures synthesized by these principles not only fit naturally to the surface geometry, but also visually reveal, even reinforce, the shape’s essential characteristics. We call these feature-aligned shape texturing. Our technique is fully automatic, and introduces two novel technical components in vector field-guided texture synthesis: an algorithm that orients the salient curves on a surface for constrained vector field generation, and a feature-to-feature texture optimization.
Download: Feature-Aligned Shape Texturing code
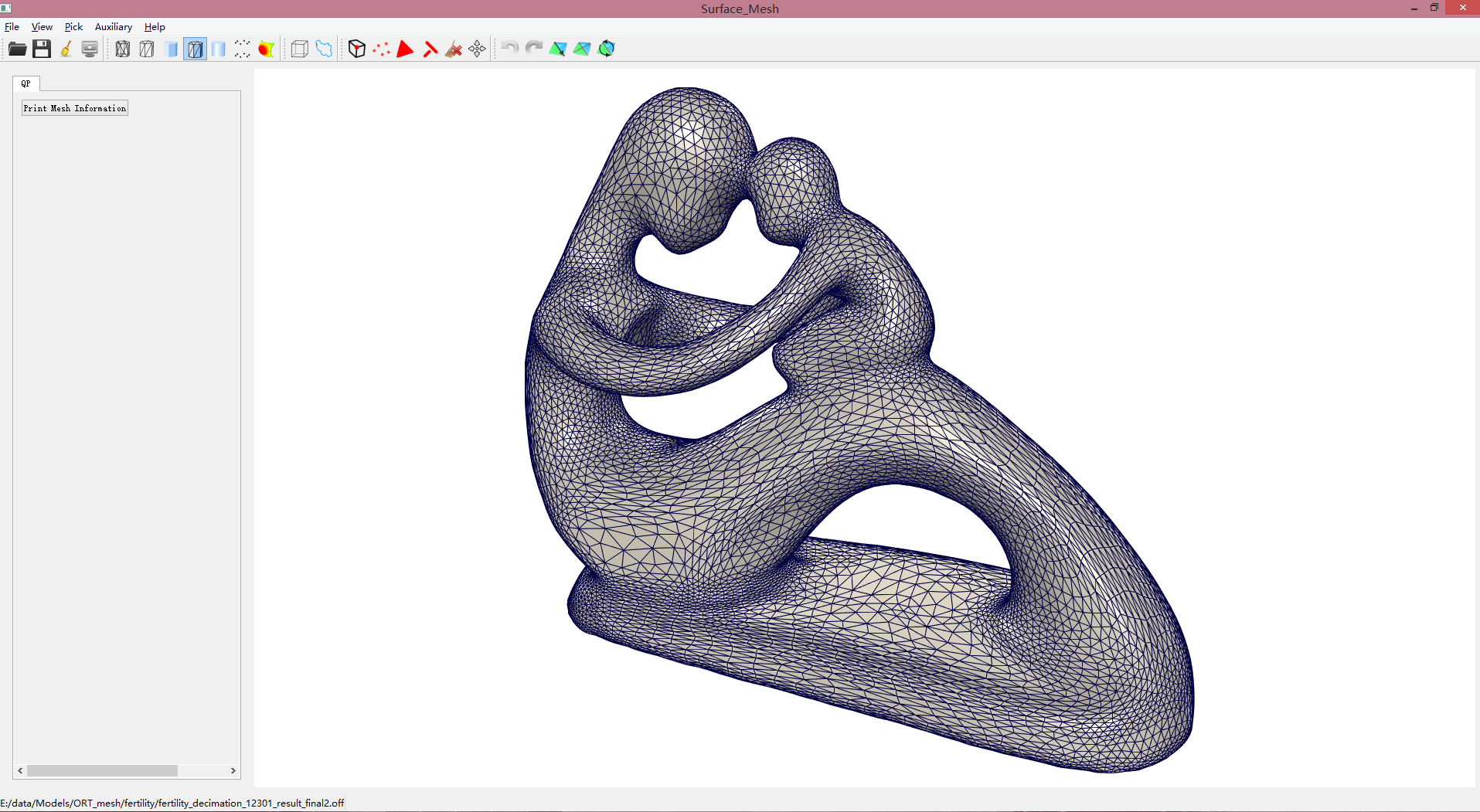
Surface Mesh Framework
We provide a simple code framework for surface mesh processing.This framework mainly contains following functions:
1. Open and save mesh file. We support general polygon mesh, such as traingle and quad mesh.
2. Basic rendering modes. Especially combining the wireframe and flat shading modes is very userful for doing geometric computing research.
3. Capture rendering region. Save the rendering region as images.
4. Pick point, vertex, edge, face on the input mesh.
Third party librires: OpenMesh and Qt. Rencently it is comppiled with Visual Studio 2013.
Download: Surface_Framework
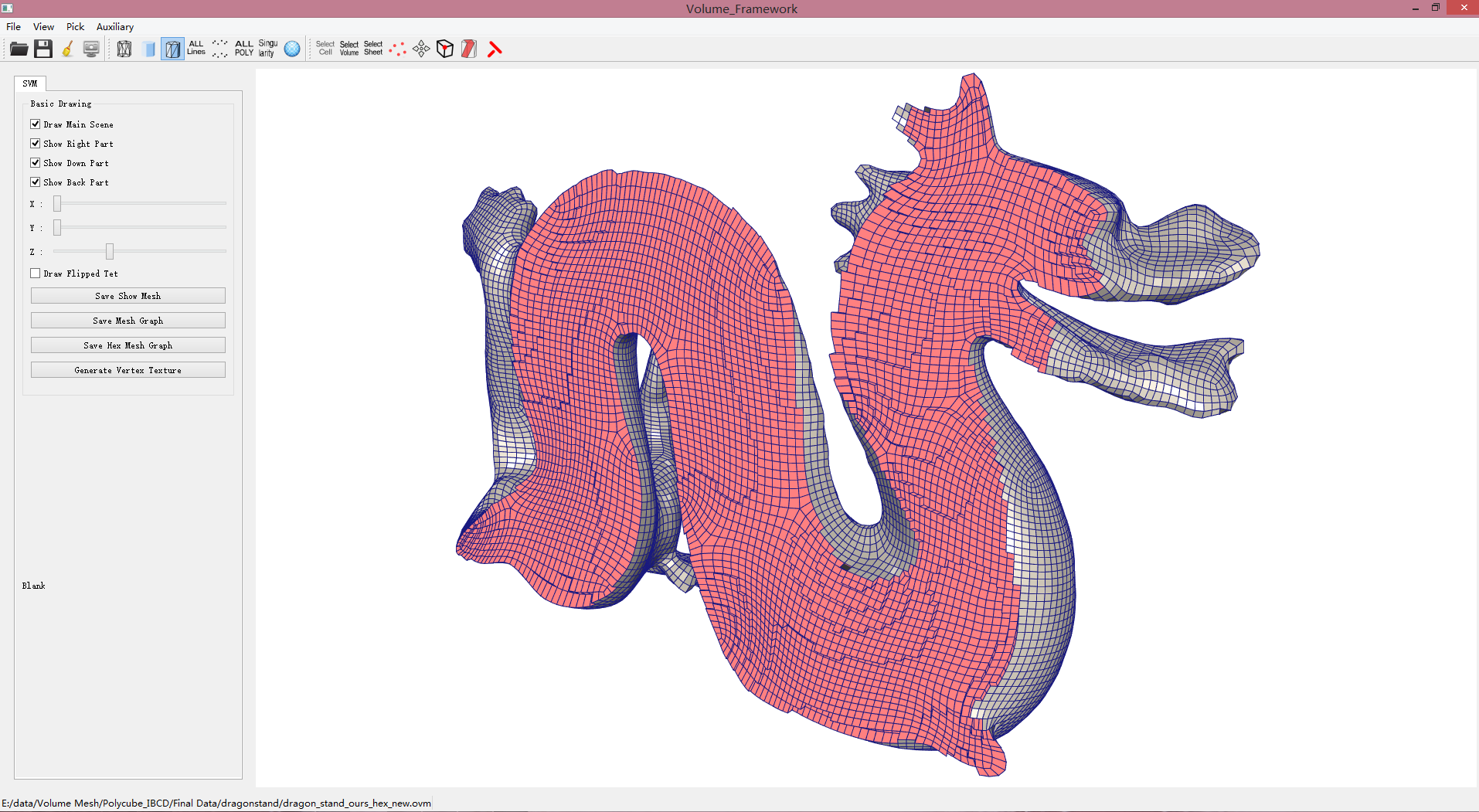
Volumetric Mesh Framework
We provide a simple code framework for volumetric mesh processing.This framework mainly contains following functions:
1. Open and save mesh file. We support tetrahedral and all-hex mesh in "OVM" file format. This format is supported by OpenVolumeMesh. You can transfer the "VTK" file into "OVM" by OpenFlipper.
2. Basic rendering modes. Especially combining the wireframe and flat shading modes is very userful for doing geometric computing research. Also the interier elements can be shown by changing slider bar on the left.
3. Capture rendering region. Save the rendering region as images.
Third party librires: OpenVolumeMesh, OpenMesh and Qt. Rencently it is comppiled with Visual Studio 2013.
Download: Volume_Framework
Download: some OVM models
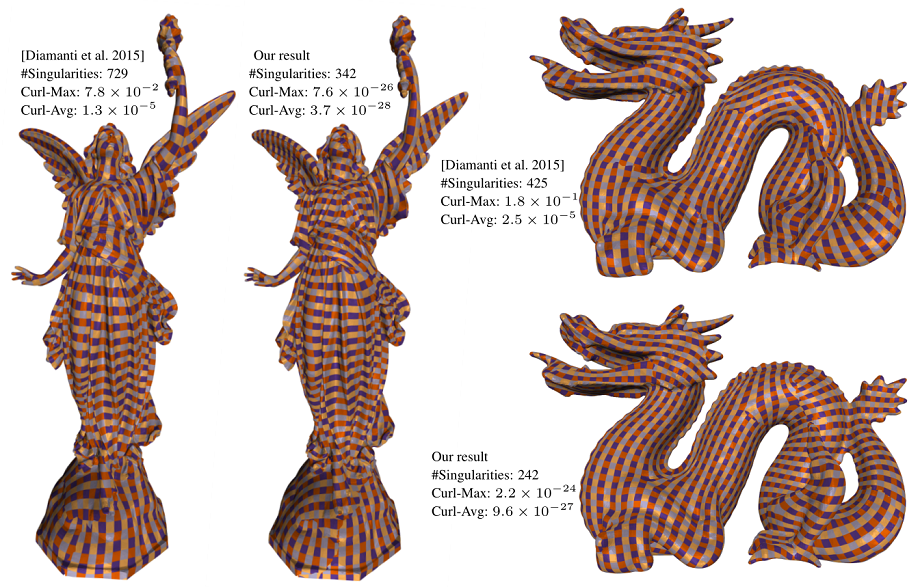
Simplex Assembly.
Global seamless parameterization. Compared with [Diamanti et al. 2015], our method maintains the original singularities and has much lower edge-curl values.
Download: Simplex Assembly code
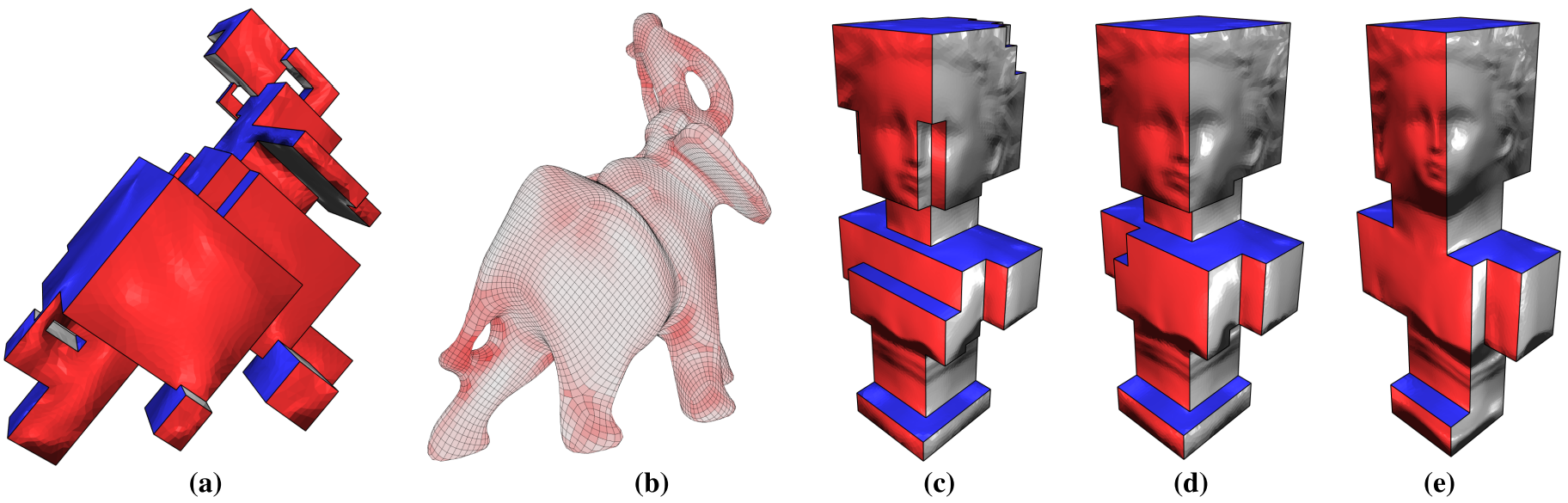
PolyCube (Part)
The volumetric PolyCube-map for the Elephant model (48k tetrahedrons). Our method took 17 seconds to achieve the PolyCube-map whose maximum isomeric distortion is \(11.7\) and the number of corners is 176. (b) The all-hex meshing result from (a). The hexahedral mesh has 46994 hexes, and the minimal and average scaled Jacobian are 0.231 and 0.887. The hexes are color-coded by their scaled Jacobian values, with white being optimal. PolyCube-maps for the Buste model using different Gaussian smoothing kernel \(\sigma\) are shown in (c), (d) and (e). From (c) to (e), the results have 128 (\(\sigma = \bar{l}_e\) where \(\bar{l}_e\) is the average boundary edge length of the input mesh), 72 (\(\sigma = 1.5\,\bar{l}_e\)) and 36 (\(\sigma = 2\,\bar{l}_e\)) corners and the average isometric distortions are 1.50, 1.53 and 1.57, respectively.
Download: PolyCube (part of the code)
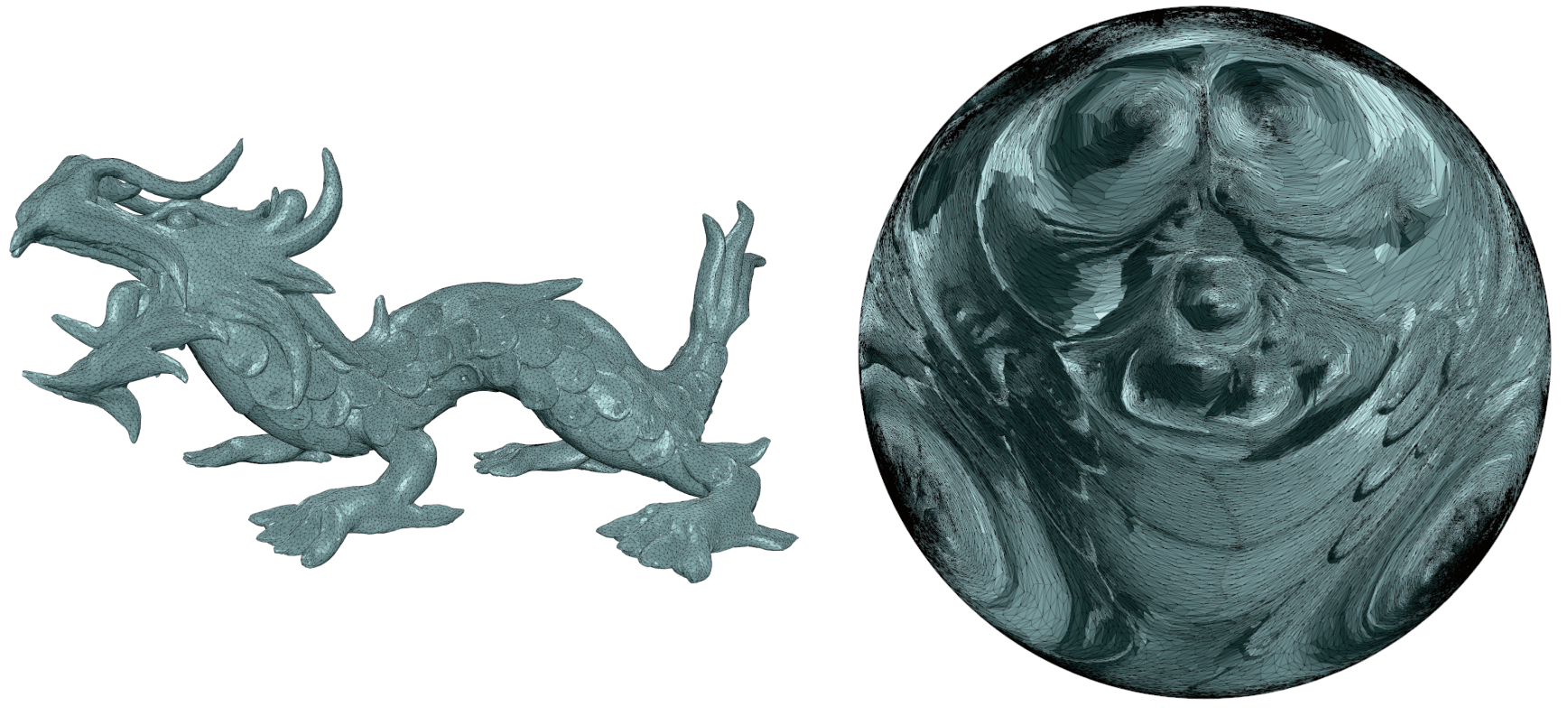
Low isometric distortion spherical parameterizations
The left mesh is the input genus-0 surface and the right one is the output spherical parameterization result, that is generated by our AHSP method.
Download: AHSP code
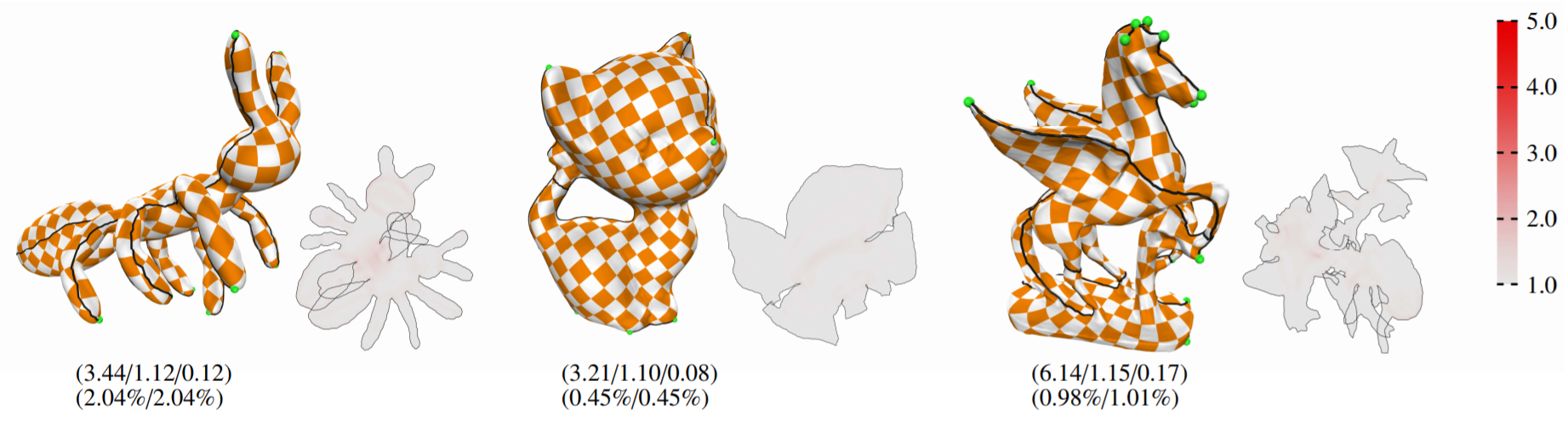
Sphere-based cut construction for planar parameterizations
Planar parameterizations of three models. Our constructed cuts are shown by black lines, and the feature points of our clustered regions are shown by green points. The parameterizations are generated by AQP [Kovalsky et al. 2016]. The isometric distortion metric (which is defined in Section 4) of each triangle is colored with white being optimal, and the models are textured by a checkerboard image. The first line of the text below the mesh indicates the maximum, average and standard deviation of the isometric distortion over all triangles, and the second line indicates the proportions of edge number and edge length of the cut.
Download: cut construction code
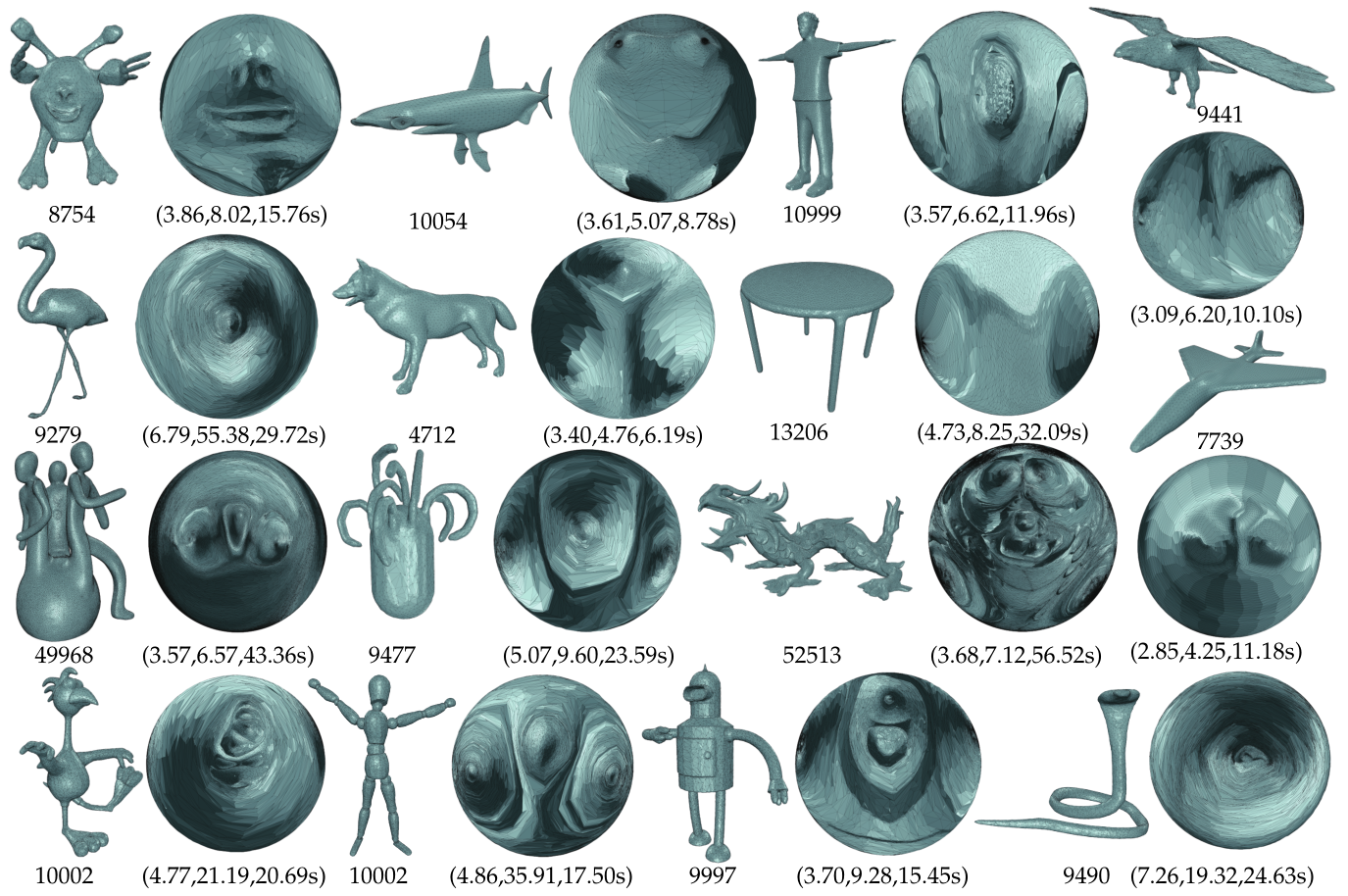
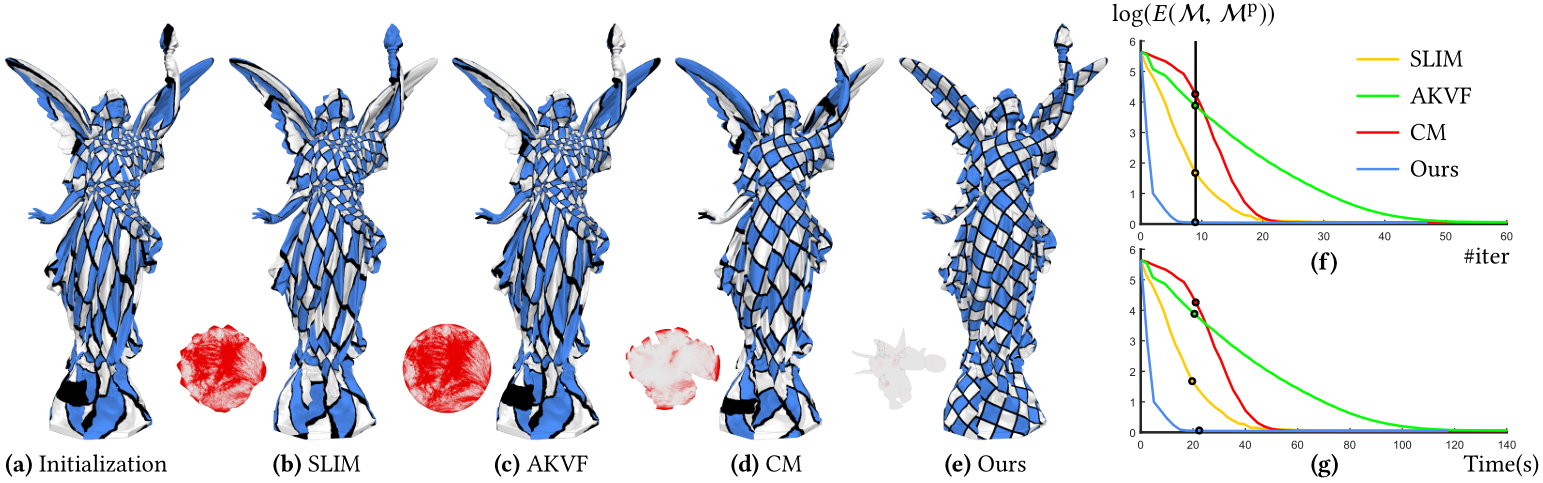
Progressive parameterizations
Parameterizing a disk topology mesh (1792000 triangles) with low isometric distortion and no foldovers by optimizing the symmetric Dirichlet energy. Starting from the same bijective initialization [Tutte 1963] (a), the energy is measured during the optimization process. The figure (b - e) shows a snapshot of the state each method achieved at the ninth iteration marked on the graph (f). The corresponding time in seconds is marked on the graph (g). The color of the triangles from the parameterized meshes encodes the symmetric Dirichlet energy metric, with white being optimal. Our approach achieves much better efficiency than the competitors including SLIM [Rabinovich et al. 2017], AKVF [Claici et al. 2017], and CM [Shtengel et al. 2017]. In order to achieve our result in (e), SLIM, AKVF and CM require 144, 81, and 17 more iterations and 314.60, 184.45, and 38.65 more seconds, respectively.
Download: Progressive parameterizations code
Datasets
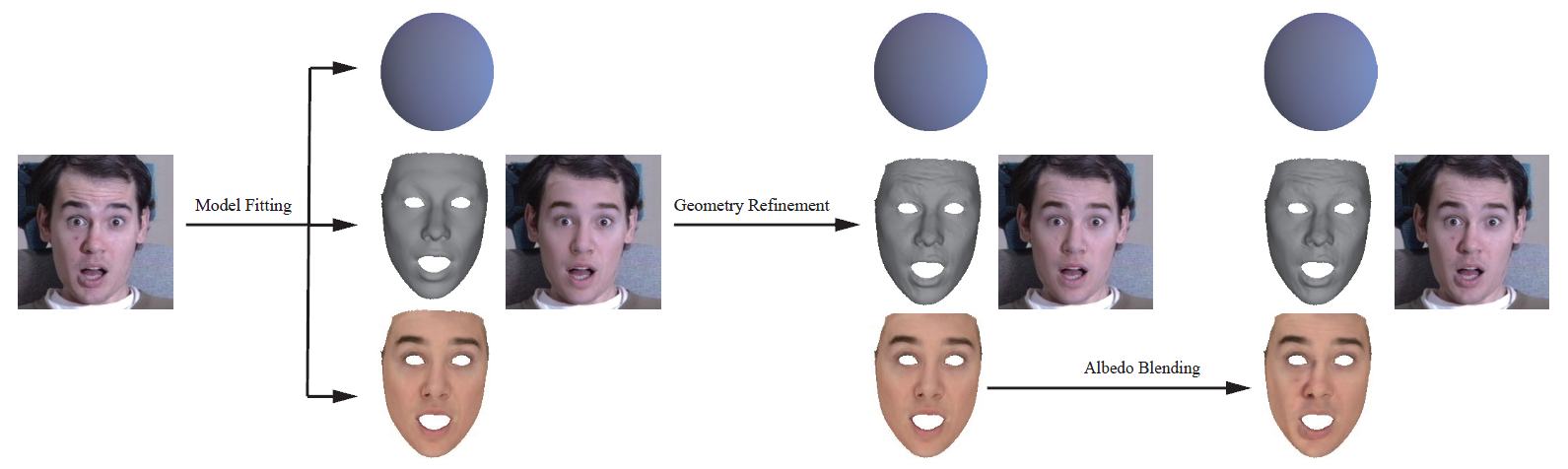
CNN-based Real-time Dense Face Reconstruction with Inverse-rendered Photo-realistic Face Images
This dataset contains CoarseData and FineData augmented from 3131 images of 300-W with the method described in the paper 3DFaceNet: Real-time Dense Face Reconstruction via Synthesizing Photo-realistic Face Images. CoarseData is constructed by varying poses and expressions of the original images. FineData is constructed by transferring details from other images to the original images. We augment each image 30 times for both CoarseData and FineData.
Download: Training data
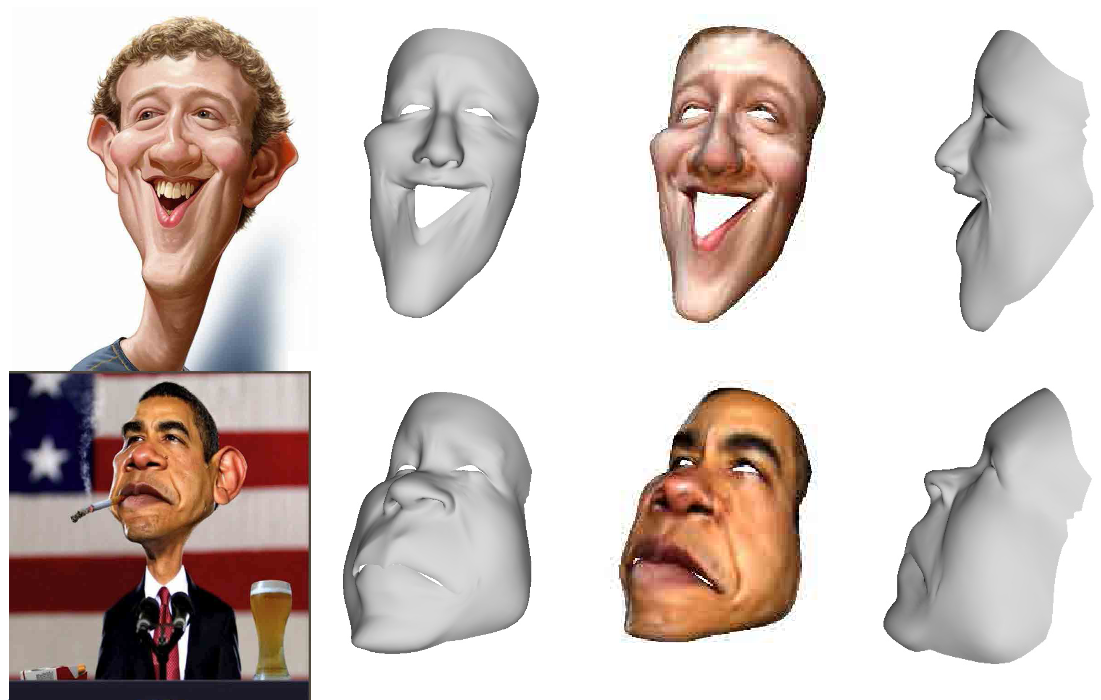
Alive Caricature from 2D to 3D
This repository contain the caricature images with corresponding landmark in paper: Alive Caricature from 2D to 3D. The Caricature_w_landmark folder contains the caricature images with its landmarks. We named them by number. e.g. 1.jpg with its landmarks file named 1.txt.
Download: Training data
Structure Completion for Facade Layouts
Test data for the paper "Structure Completion for Facade Layouts".
Download: Structure Completion for Facade Layouts
Multi-Scale Partial Intrinsic Symmetry Detection
Test data for the paper "Multi-Scale Partial Intrinsic Symmetry Detection.
Download: Multi-Scale Partial Intrinsic Symmetry Detection
Animated Construction of Line Drawings
Test data for the paper "Animated Construction of Line Drawings.
Download: Animated Construction of Line Drawings
Projective Feature Learning for 3D Shapes with Multi-View Depth Images
Test data for the paper "Projective Feature Learning for 3D Shapes with Multi-View Depth Images.
Download: Projective Feature Learning for 3D Shapes with Multi-View Depth Images
Spherical parameterizations of 5181 genus zero meshes
We provide 5181 meshes and their spherical parameterizations on Dropbox.
Download: Spherical parameterizations data
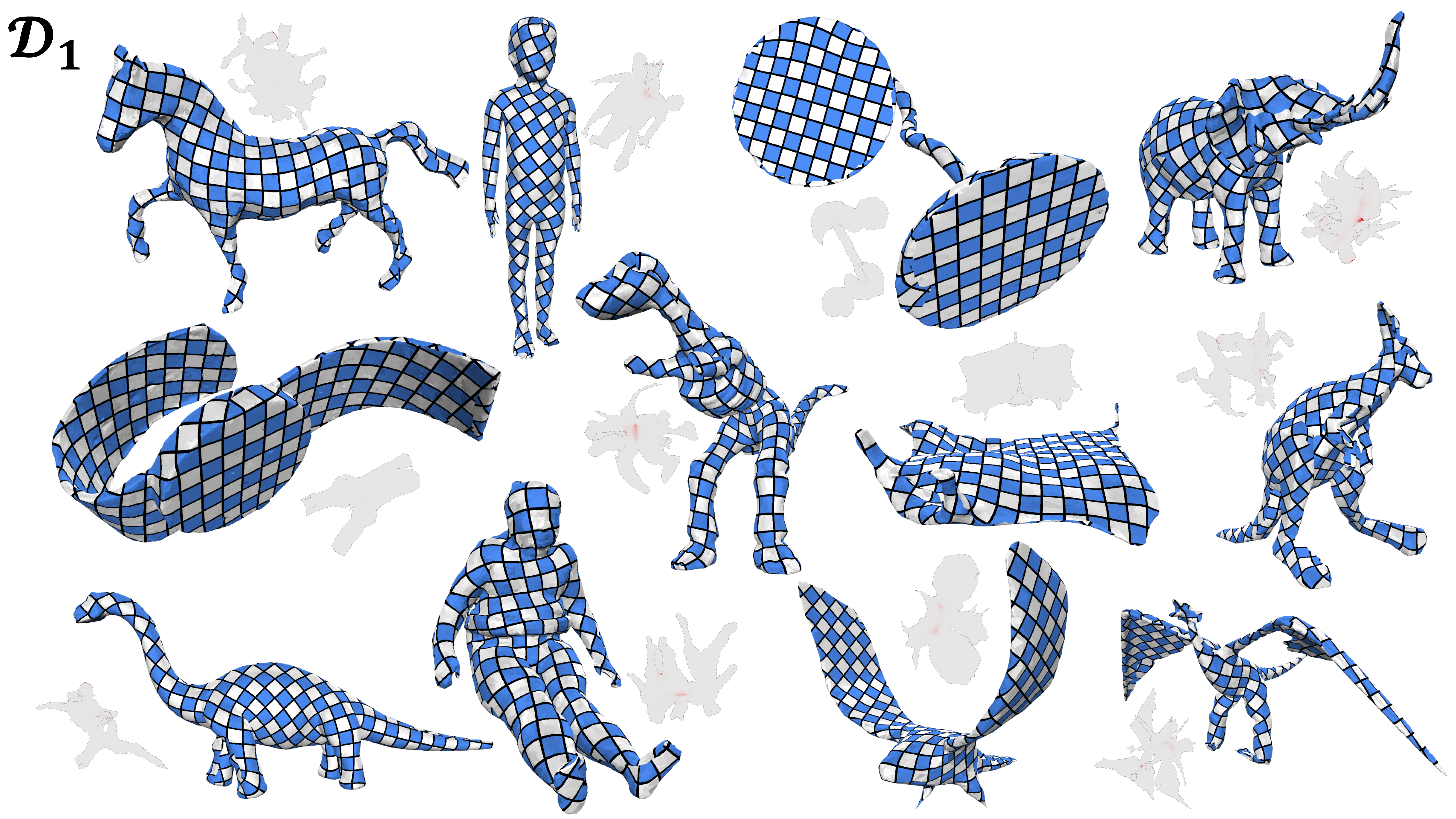
Data Set for Parameterizations
This large testing benchmark contains 20712 meshes. It starts from well cut meshes D1, continues with moderately bad ones D2, and ends with extremely challenging examples D3. If you use our data set, please cite [Liu et al. 2018] and [Chai et al. 2018].
Download: Planar parameterizations data
Data Set for PolyCube-Map
Data Set containts 106 models which vary from natrual objects to CAD models. It is mainly based on the benchmark of global seamless parameterization and mesh segmentation.
Download: PolyCube-Map data